Dog Age Calculator
Discover how old your dog really is in human years with our Dog Age Calculator! Dogs age differently based on their size, breed, and life stage, which means the traditional "seven dog years to one human year" rule isn't accurate for every pup.
This tool provides a science-backed calculation that translates your dog's age into human years, giving you valuable insight into their growth, maturity, and overall health needs.

To calculate dog years to human years, enter your dog's age and breed and press Submit.
How It Works: Dog Age Calculator
The Dog Age Calculator by Holistapet is a user-friendly tool designed to help pet owners better understand their dog's age in human years. Dogs age at different rates depending on their size, breed, and overall health, so a one-size-fits-all approach doesn't give the full picture.
That's where this calculator comes in—it uses scientific formulas to accurately assess your furry friend's age and life stage.
Here's how to use it:
1. Enter Your Dog's Age
Input your dog's age in months or years for a precise calculation.
2. Select Your Dog's Breed
Choose your dog's breed from a dropdown menu. The calculator factors in breed-specific aging patterns to ensure accuracy.
3. Get the Results
Instantly view your dog's human-equivalent age and life stage—puppy, adult, or senior.
Why Use a Dog Age Calculator?
Understanding your dog's age in human years is more than just a fun fact—it's a helpful tool for tailoring their care. Knowing your pet's life stage can guide you in choosing the right diet, exercise routine, and veterinary care.

Science Behind the Dog Age Calculator
The Holistapet Dog Age Calculator takes into account factors like:
- Breed-Specific Aging: Small dogs, like Chihuahuas, age differently than large breeds, such as Labradors or Great Danes.
- Size and Weight: Larger dogs typically age faster and have shorter lifespans, while smaller breeds mature slower and live longer.
- Life Stages: The calculator uses the latest research to map dog years to human years based on developmental milestones.
Whether you're raising a tiny Chihuahua or a giant Great Dane, our Dog Age Calculator considers breed-specific aging patterns to give you the most precise results.
Start Calculator
Dog Age Chart by Breed Size
This chart is a quick reference guide for understanding the correlation between a dog's age and its equivalent human years based on size and weight. It allows pet owners to:
- Determine their dog's human-equivalent age.
- Gain insights into the aging process for different types of dogs (e.g., X-Small: 0-10 lbs, Small: 11-25 lbs, etc.).
- Identify the life stage of their dog (puppy, adult, senior).
By integrating the Dog Age Calculator, pet owners can make informed decisions about their pet's care, diet, and veterinary needs, ensuring their furry companions a healthier and happier life.
| Size/Weight Range | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-Small (0-10 lbs) | Small (11-25 lbs) | Medium (26-50 lbs) | Large (51-100 lbs) | Giant (101+ lbs) | |
| Dog Age (Years) | Age in Human Years | ||||
| 1 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 12 |
| 2 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 22 |
| 3 | 28 | 29 | 28 | 28 | 31 |
| 4 | 32 | 34 | 32 | 32 | 40 |
| 5 | 36 | 39 | 36 | 36 | 49 |
| 6 | 40 | 44 | 42 | 45 | 59 |
| 7 | 44 | 48 | 47 | 50 | 68 |
| 8 | 48 | 52 | 51 | 55 | 77 |
| 9 | 52 | 57 | 56 | 61 | 86 |
| 10 | 56 | 61 | 60 | 66 | 96 |
| 11 | 60 | 66 | 65 | 72 | 105 |
| 12 | 64 | 70 | 69 | 77 | 114 |
| 13 | 68 | 75 | 74 | 83 | 123 |
| 14 | 72 | 79 | 78 | 88 | 132 |
| 15 | 76 | 84 | 83 | 94 | 141 |
| 16 | 80 | 88 | 87 | 99 | 150 |
| 17 | 84 | 93 | 92 | 105 | 159 |
| 18 | 88 | 97 | 96 | 110 | 168 |
| 19 | 92 | 102 | 101 | 116 | 177 |
| 20 | 96 | 106 | 105 | 121 | 186 |

How Long Do Dogs Live: Common Breeds
Understanding the lifespan of popular dog breeds helps pet owners provide tailored care and enjoy the most time with their furry companions. Here's a breakdown of lifespans for some of the most well-known breeds.
Small Breeds
Small dog breeds tend to live longer due to slower aging and reduced physical strain on their bodies.
- Chihuahua: 14–16 years
- Dachshund (Weiner Dog): 12–16 years
- Maltese: 12–15 years
- Shih Tzu: 10–16 years
- Teacup Dogs: 12–16 years (varies depending on breed)
- Maltipoo: 12–15 years
- Corgi: 12–15 years
- French Bulldog: 10–12 years

Medium Breeds
Medium breeds balance size and health, with moderately long lifespans.
- Australian Cattle Dog (Blue or Red Heeler): 12–16 years
- Beagle: 12–15 years
- Portuguese Water Dog: 10–14 years
Mixed Breed Dogs (Medium Size): 10–15 years

Large Breeds
Large dog breeds age more quickly due to their size but remain among the most popular choices for families.
- Labrador Retriever: 10–12 years
- Boxer: 10–12 years
- German Shepherd: 9–13 years
- Husky: 12–14 years
- Pitbull: 10–14 years
- Hound Dogs (varies by type): 10–14 years
- Cattle Dogs: 10–13 years

Giant Breeds
Giant breeds have shorter lifespans due to their rapid growth and size-related health challenges.
- Great Dane: 7–10 years
- Bernese Mountain Dog: 6–8 years
- Great Pyrenees: 10–12 years
- Wolf Dogs: 10–12 years
Why Do Small Dogs Live Longer Than Larger Dogs?
Small dogs tend to live longer than large dogs due to differences in growth rates, metabolic demands, and susceptibility to age-related diseases. This trend is rooted in biological and physiological factors influencing dog breeds' aging process.
1. Growth and Aging Rates
- Larger dogs grow rapidly during their first year, placing more stress on their bodies, especially their bones and joints.
- Rapid growth can lead to earlier onset of age-related conditions, such as arthritis or heart disease, shortening their lifespan.
2. Metabolic Differences
- Smaller dogs have slower metabolic rates relative to their size, which helps reduce cellular damage caused by oxidative stress.
- In contrast, larger dogs expend more energy to sustain their bodies, leading to faster wear and tear on their organs.
3. Heart and Organ Stress
- Larger breeds have proportionally smaller hearts for their body size, making it harder for their cardiovascular system to keep up with their energy demands over time.
- This strain increases the risk of conditions like dilated cardiomyopathy and other chronic illnesses, which can reduce lifespan.
4. Genetic and Evolutionary Factors
- Smaller breeds are often selected for longevity through breeding practices that favor robust health and long life.
- Larger breeds, like Great Danes or Mastiffs, were historically bred for size and strength, sometimes at the cost of longevity.
Understanding why small dogs tend to live longer provides valuable insights into how size and biology impact a dog's lifespan. However, lifespan is only part of the story—your dog's care needs also change dramatically depending on its life stage. Identifying your dog's life stage, from playful puppyhood to golden senior years, is crucial to ensuring it thrives at every phase.
Let's explore how to determine your dog's life stage and what it means for their health and well-being.
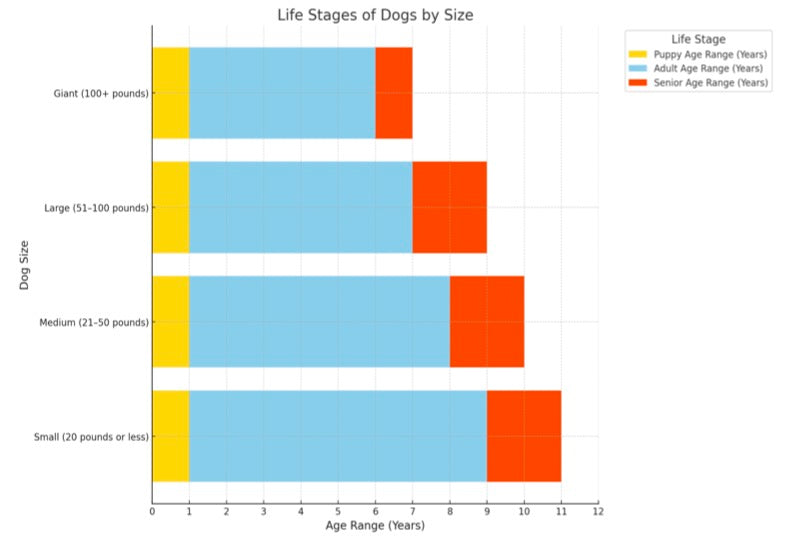
Identifying Your Dog’s Life Stage
Understanding your dog's life stage is vital for meeting their specific needs at each phase of life. Dogs age differently based on size, with larger breeds aging faster than smaller ones.
Use the Dog Age Calculator to pinpoint your dog's human-equivalent age and identify their life stage.
Start Calculator
Why Knowing Your Dog’s Life Stage Matters
- Puppy Stage: Focus on growth with nutrient-rich diets and training.
- Adult Stage: Provide balanced exercise, regular checkups, and maintenance diets.
- Senior Stage: Prioritize joint health, a senior-specific diet, and more frequent vet visits.
With the Dog Age Calculator, you can ensure your furry friend receives age-appropriate care for a long, happy, and healthy life!
Frequently Asked Questions:
How Do You Calculate a Dog’s Age?
How Do You Calculate a Dog’s Age?
A general formula can be used to calculate a dog's age, but it varies depending on breed and size. For small and medium-sized breeds, the first year equals approximately 15 human years, the second year equals about 9 human years, and each subsequent year equals 4–5 human years. Larger breeds age faster, so their first year equals 15 human years, and each year after equals 7–8 human years. Using a Dog Age Calculator provides the most accurate results by considering breed-specific aging.
Is There a Way to Tell a Dog's Exact Age?
Is There a Way to Tell a Dog's Exact Age?
While it's difficult to determine a dog's exact age, veterinarians can estimate it using: Teeth Condition: Puppies have baby teeth, while older dogs show wear or tartar buildup. Fur Changes: Older dogs often develop gray hairs around the muzzle. Activity Levels: Senior dogs tend to be less active. Eye Clarity: Cloudy eyes can indicate advanced age. A Dog Age Calculator can provide an approximate human-equivalent age for better insights.
What Is the Oldest Dog to Ever Live?
What Is the Oldest Dog to Ever Live?
The oldest dog to ever live was Bobi, a Rafeiro do Alentejo from Portugal, who reached 31 years and 165 days as of 2023. His extraordinary lifespan highlights the importance of genetics, a stress-free environment, and excellent care in promoting longevity.
How Accurate Is the Age Test for Dogs?
How Accurate Is the Age Test for Dogs?
Age tests for dogs, such as Holistapet's Dog Age Calculator, are accurate for providing human-equivalent ages based on breed, size, and life stage. However, they are estimates. Advanced tools like DNA-based tests can analyze telomere length to determine a dog's exact biological age, offering insights into a dog's cellular age and overall health.
Why Do Dogs Age So Quickly?
Why Do Dogs Age So Quickly?
Dogs age quickly due to the following: Metabolism: Faster cellular processes and higher metabolic rates lead to quicker aging. Evolution: Dogs are designed to mature rapidly for survival. Genetics: Shorter telomeres in dogs' DNA lead to faster cellular aging.
How Can You Tell if Your Dog is Really Old?
How Can You Tell if Your Dog is Really Old?
Signs your dog is entering old age include: Slower Movement: Difficulty climbing stairs or getting up. Gray Fur: Especially around the muzzle. Behavioral Changes: Increased sleep or confusion. Weight Changes: Unexplained loss or gain. Health Issues: Arthritis, cloudy eyes, or dental problems. Please consult your vet to assess their life stage and adjust care.







![Probiotics For Dogs [Soft Chews] - HolistaPet](http://www.holistapet.com/cdn/shop/files/Probiotic-Infographic-1_472d7a29-e30c-435a-9638-1365d8c3a9f9.jpg?v=1725384841&width=104)















